Bananas are one of the most important tropical fruits in the global food system, consumed daily by millions of people and traded across nearly every major international market. While often seen as a single familiar fruit, bananas actually include many types of bananas, each shaped by origin, cultivation method, nutritional profile, and commercial purpose.
Today, different types of bananas serve distinct roles—from fresh consumption and cooking to food processing and export programs. Understanding how banana varieties differ in taste, texture, ripening behavior, and market suitability helps consumers, retailers, and importers make informed decisions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of banana origins, major types of bananas, nutrition, and how each variety fits into modern global markets.

1. About Bananas: A Global Tropical Staple
Bananas are more than a familiar fruit—they are a foundational crop in many tropical economies and a daily food source for populations worldwide. From local markets in Asia and Africa to large-scale retail systems in the United States and Europe, bananas play a critical role in food availability and affordability.
What makes bananas unique is their ability to combine agricultural efficiency with mass consumer appeal. They can be produced continuously throughout the year in tropical climates, harvested at a controlled maturity stage, and transported long distances while maintaining quality. This balance between biological resilience and commercial practicality has positioned bananas as one of the most reliable fruits in global trade.
Today, bananas support multiple market segments at once: fresh retail programs, foodservice operations, and large-scale food processing. Their role extends beyond nutrition, influencing supply chains, pricing stability, and international sourcing strategies across the fruit industry.

2. Why Understanding Types of Bananas Matters
While bananas are often treated as a single product by consumers, the reality is far more complex. Different types of bananas are developed, selected, and traded for very specific purposes, and these differences directly affect how bananas are grown, shipped, sold, and consumed.
In commercial markets, choosing the right banana type impacts everything from shelf life and ripening control to flavor consistency and handling efficiency. Some banana types are better suited for fresh eating, while others perform best in cooking, processing, or extended storage. These distinctions are especially important for retailers and importers operating across long-distance supply chains.
Understanding the characteristics of different banana types helps buyers reduce risk, optimize logistics, and meet consumer expectations more effectively. For this reason, banana variety selection is not only an agricultural decision—it is a strategic factor in modern fruit trade.

3. Popular Banana Varieties Around the World
There are hundreds of banana varieties cultivated worldwide, but only a few dominate commercial and export markets.
Cavendish Banana – Backbone of the Global Banana Trade
Cavendish banana forms the backbone of the international banana industry, particularly in the US and European retail markets. Its commercial success lies in consistency—uniform size, predictable ripening, and strong performance during long-distance transportation.
From a buyer’s perspective, Cavendish banana offers operational reliability. Its peel durability and controlled ripening characteristics allow retailers to manage inventory efficiently while minimizing shrinkage.
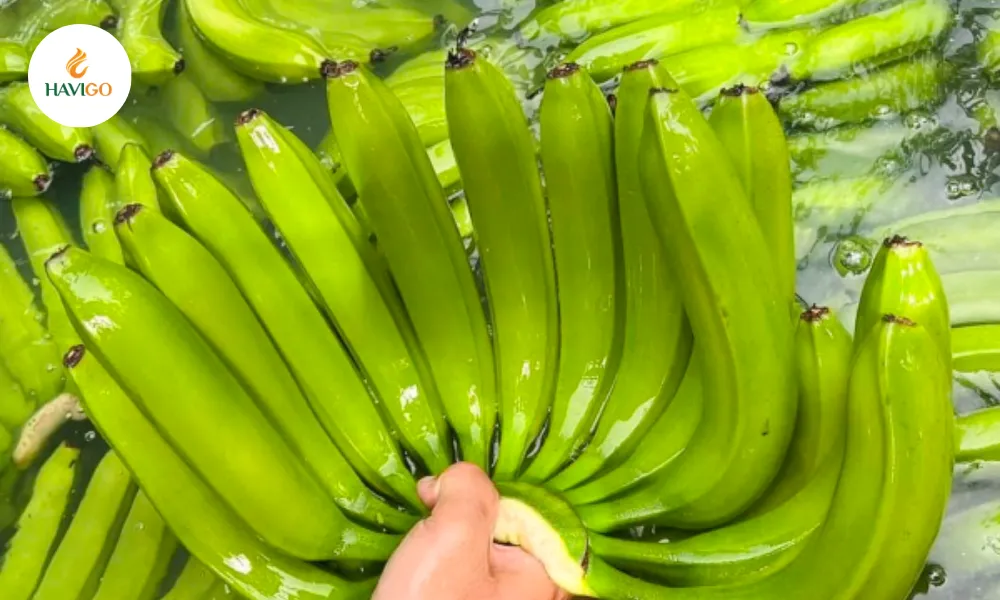

Plantain – Functional Banana for Cooking and Processing
Plantain belongs to the cooking banana category and serves a completely different market purpose than dessert bananas. Its higher starch content and firm structure make it suitable for heat-based applications rather than fresh snacking.
In the US, plantain demand is driven largely by ethnic retail chains, foodservice operators, and processors seeking stable texture and cooking performance.

Red Banana – Specialty Variety for Premium Segments
Red banana is positioned as a specialty variety rather than a mass-market product. Its distinctive peel color and richer flavor profile help retailers differentiate their fruit assortment and target consumers seeking variety beyond standard yellow bananas.
Due to its niche positioning, red banana is typically supplied in smaller volumes with higher unit value.

Regional Banana Cultivars – Niche Opportunities
Beyond mainstream varieties, many producing countries cultivate regional banana types designed for local consumption or limited export programs. These cultivars often appeal to specialty buyers focused on authenticity, flavor diversity, or cultural relevance.

4. Banana Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits
Bananas are not only delicious and convenient—they are also a nutrient-rich fruit that offers a range of health benefits. A medium banana (about 118 g) provides a balanced mix of carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and essential minerals with just about 105 calories, making it a wholesome addition to daily meals.
Key Nutrition Facts (per medium banana)
- Calories: ~105 kcal
- Carbohydrates: ~27–29 g (mostly natural sugars and fiber)
- Dietary Fiber: ~3.1 g
- Protein: ~1.3 g
- Fat: ~0.4 g (very low)
- Potassium: ~422 mg
- Vitamin B6: ~0.4 mg
- Vitamin C: ~10–12 mg
- Magnesium & Manganese: Present in beneficial amounts
This nutrient profile highlights bananas as low-fat, fiber-rich, and rich in key micronutrients that support overall health.

Health Benefits of Bananas
Heart and Blood Pressure Support
Bananas are an excellent source of potassium, a mineral essential for heart function and fluid balance. Potassium helps the body counteract the negative effects of sodium, which can help promote healthy blood pressure and reduce strain on blood vessels.
Digestive Health
The fiber in bananas includes both pectin and resistant starch (especially in less ripe fruit). These fibers help slow digestion, support healthy gut bacteria, and may aid regular bowel movements. Pectin and resistant starch also contribute to a moderate glycemic response, making bananas a sensible carbohydrate choice for sustained energy.
Natural Energy Boost
Bananas are carbohydrate-rich, providing quick-release natural sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose. This makes them an ideal pre- or post-workout snack, delivering accessible energy without added fat. Healthline
Vitamins and Antioxidants
Bananas contain B6 and C vitamins and compounds like dopamine and catechins that function as antioxidants. These nutrients help neutralize free radicals, support immune function, and contribute to cellular health. Healthline+1
Weight and Blood Sugar Considerations
Despite their sugar content, bananas have a moderate glycemic index (around 42–51), meaning they provide a steady release of energy rather than causing rapid spikes in blood sugar. This effect, combined with fiber that promotes satiety, makes bananas a favorable choice for many balanced diets.
How Ripeness Affects Nutrition
The nutritional composition of bananas changes as they ripen. In greener bananas, more carbohydrates are in the form of resistant starch, which functions similarly to fiber and feeds beneficial gut bacteria. As bananas ripen and sugars increase, the resistant starch decreases, leading to a softer texture and sweeter taste.
5. Uses of Bananas in Fresh Consumption and Processing
Fresh Consumption
Fresh bananas are commonly enjoyed as:
- Ready-to-eat snacks
- Ingredients in smoothies and shakes
- Additions to breakfast bowls and cereals
In the US market, demand is strongest for bananas that ripen evenly, maintain shelf appearance, and deliver consistent flavor.
Food Processing and Industrial Uses
Different types of bananas are also widely used in processing, including:
- Dried banana chips
- Banana puree for baby food and beverages
- Frozen bananas for smoothies and desserts
- Bakery fillings and snack bars
This wide application range supports stable, year-round demand across retail and industrial sectors.

6. Banana Supply and Export for International Markets
Supplying bananas to global markets requires far more than high production volume. Export-grade bananas must meet strict technical, visual, and logistical standards to ensure quality, safety, and shelf performance from origin to destination—especially in demanding markets such as the United States and Europe.
1. Harvesting at the Correct Maturity Stage
Bananas for export are harvested while still green but at a precisely defined physiological maturity, typically measured by fruit age, size, and pulp-to-peel ratio.
Harvesting too early can result in:
- Poor flavor development
- Uneven ripening
- Lower consumer acceptance
Harvesting too late increases the risk of:
- Premature ripening
- Bruising and mechanical damage
- Shortened shelf life during transit
Professional exporters follow strict maturity indexes to ensure bananas can ripen evenly after arrival while maintaining firmness during long-distance transport.
2. Post-Harvest Handling and Controlled Ripening Management
Immediately after harvest, bananas undergo a series of post-harvest processes designed to protect quality and extend shelf life, including:
- De-handing and trimming under hygienic conditions
- Washing and latex removal
- Sorting by size and appearance
- Packing under controlled environments
For international trade, ripening control is critical. Bananas are shipped green and later ripened at destination using controlled ethylene exposure. Proper ripening management allows importers and retailers to:
- Time product availability accurately
- Reduce shrink and waste
- Deliver consistent color and taste to consumers
3. Cold-Chain Logistics from Farm to Destination
Maintaining an uninterrupted cold chain is essential for banana exports. Export-grade bananas are typically stored and transported at 13–14°C (55–57°F) to slow respiration and prevent premature ripening.
A reliable cold-chain system includes:
- Pre-cooling at packing facilities
- Temperature-controlled containers
- Continuous monitoring during ocean freight
- Careful handling at ports and ripening centers
Any temperature fluctuation can directly affect shelf life, appearance, and eating quality—making logistics management a decisive factor in successful banana supply.
4. Compliance with Food Safety and Import Regulations
Bananas supplied to international markets must comply with strict food safety, phytosanitary, and quality standards, particularly for the US market.
Key compliance areas include:
- Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) at farm level
- Residue monitoring and traceability
- Pest and disease control
- Proper labeling and documentation
Buyers increasingly prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate consistent compliance, transparency, and long-term reliability rather than spot-market sourcing.
Reliable Banana Supply from HAVIGO
HAVIGO supplies export-grade Cavendish bananas for international markets, offering two common packaging formats:
- Hand pack bananas: Whole hands, ideal for wholesalers and repacking operations
- Cluster pack bananas: 6–8 fingers per cluster, suitable for retail-ready programs
By coordinating with experienced growers and managing post-harvest handling, HAVIGO supports consistent quality, shelf performance, and supply stability for US and global buyers.

7. Why Bananas Remain a Global Staple Fruit
The global success of bananas is driven by a unique combination of advantages:
- Strong consumer familiarity
- Affordable pricing compared to other tropical fruits
- Efficient handling and transportation
- Flexible use across fresh, foodservice, and processing channels
From household kitchens to international trade networks, bananas remain an essential fruit in the global food system.
8. FAQs About Types of Bananas
What are the main types of bananas?
The most common types include Cavendish bananas, plantains, red bananas, and Lady Finger bananas.
How many types of bananas are there?
There are hundreds of banana varieties worldwide, though only a small number dominate commercial trade.
Which banana is best for cooking?
Plantains and other cooking bananas are best for frying, boiling, and savory dishes.
Which banana is most common in US supermarkets?
Cavendish bananas account for the majority of bananas sold in the United States.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of bananas helps consumers, retailers, and importers make informed decisions—from everyday fresh consumption to large-scale sourcing and trade. With diverse varieties, strong nutritional benefits, and unmatched versatility, bananas continue to dominate global fruit markets.
As international demand grows, reliable sourcing and consistent quality remain key factors in successful banana programs.
Stay Connected with Havigo: Your Source for High-Quality Banana
HAVIGO Company Limited is a trusted agricultural export partner based in Vietnam, specializing in the supply of export-grade Cavendish bananas for international markets. We focus on building long-term partnerships by delivering:
- Consistent Quality Standards aligned with global import requirements
- Competitive Pricing optimized for wholesale and retail programs
- Responsive & Professional Support throughout sourcing and shipment coordination
If you are looking for a reliable banana supplier for retail, wholesale, or processing purposes, HAVIGO is ready to support your sourcing needs.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: +84 979 58 58 56
LinkedIn: HAVIGO COMPANY LIMITED