At first glance, the coconut seems simple. It’s hard, round, and filled with refreshing water and white flesh. But when people ask, “Is a coconut a fruit, a nut, or a seed?”, the answer is far more interesting than expected.

Scientifically speaking, the coconut challenges everyday food classifications. Let’s explore what a coconut truly is, how it grows, and why it stands out as one of nature’s most remarkable plant designs.
Table of Contents
The Botanical Classification of Coconut
From a botanical perspective, a coconut is classified as a drupe. A drupe is a type of fruit that has three distinct layers:
- Exocarp – the outer skin
- Mesocarp – the fibrous or fleshy middle layer
- Endocarp – a hard inner shell that protects the seed inside
Well-known examples of drupes include peaches, cherries, and olives. The coconut follows the same structural pattern, though on a much larger and tougher scale.
In the coconut’s case:
- The green or brown husk is the mesocarp
- The hard shell is the endocarp
- The white coconut meat and water support the seed within
So botanically, the coconut is clearly a fruit.
Why People Often Think Coconut Is a Nut
In everyday language, coconuts are often called nuts. This confusion comes from culinary and commercial usage rather than science.
In cooking, the word “nut” is loosely applied to any hard-shelled food with an edible interior. Since coconuts share this physical trait, they naturally fall into the nut category in kitchens and markets.
However, true nuts, such as acorns or chestnuts, do not split open and do not contain multiple layers like drupes. By botanical standards, coconuts do not meet the definition of a nut.
Is Coconut Also a Seed? Surprisingly, Yes
Here’s where the coconut becomes truly unique.
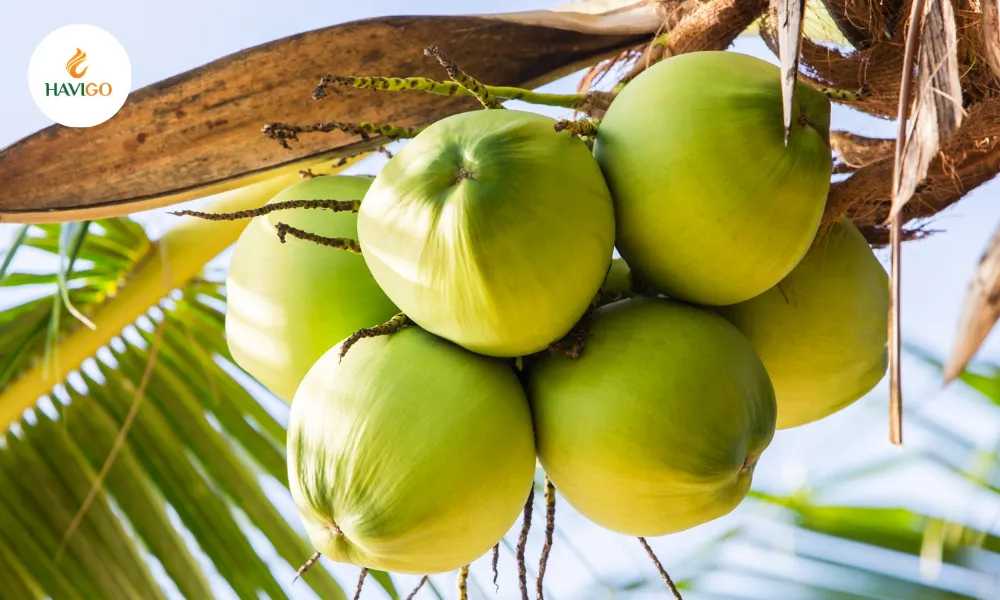
Although it is a fruit, the coconut also functions as a seed. Inside the hard shell lies everything needed for a new coconut palm to grow:
- Stored water for hydration
- Nutrient-rich meat for energy
- A germination point that allows sprouting

If a coconut falls to the ground or washes ashore, it can germinate on its own without soil or external nutrients. This dual identity as both fruit and seed is rare in the plant world.
Designed to Travel Across Oceans
One of the coconut’s most fascinating features is its ability to float.
The fibrous husk traps air, allowing coconuts to drift across oceans for thousands of kilometers. This natural design enabled coconut palms to spread across tropical coastlines long before human cultivation.
Once a floating coconut reaches land, it can take root and grow into a new palm, making the coconut one of nature’s most successful long-distance travelers.
What Makes Coconut Different from Other Fruits
Several traits make coconuts stand apart:
- They contain liquid endosperm (coconut water) instead of just solid flesh
- They can survive saltwater exposure for extended periods
- They serve as both a food source and a reproductive system
- They require 11–12 months to fully mature
Beyond their unique biological features, every bit of the coconut can be used. As a result, coconuts are often called the “Tree of Life,” capable of producing drink, fiber, food, fuel, utensils, musical instruments, and much more.
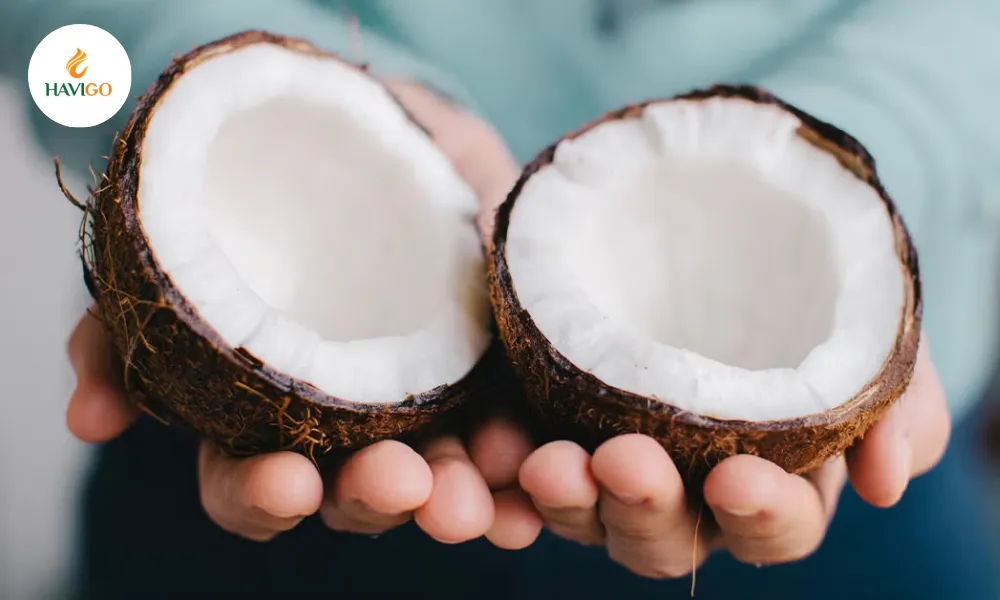

These remarkable characteristics explain why coconuts are found across tropical regions worldwide and why they play such a vital role in coastal ecosystems and human cultures.
Why Understanding Coconut Classification Matters
Knowing whether a coconut is a fruit, nut, or seed is not just a fun fact. It has real implications for:
- Agriculture and trade
- Food labeling and allergen awareness
- Botanical education
- Export standards and product categorization
For example, coconuts are generally not classified as tree nuts for allergy labeling, which is important information for consumers and food manufacturers.
Conclusion
So, is a coconut a fruit, a nut, or a seed?
The most accurate answer is:
A coconut is a fruit (specifically a drupe) that also functions as a seed.
This rare combination, along with its ocean-traveling ability and nutritional value, makes the coconut one of the most extraordinary natural products on Earth.
Behind its tough shell lies a brilliant example of botanical engineering—one that continues to support diets, economies, and ecosystems around the globe.
Stay Connected with Havigo: Your Source for High-Quality Coconut
Havigo Company Limited is your reliable agricultural export partner in Vietnam. We specialize in supplying and delivering high-quality Vietnamese agricultural products, including spices, rice, beans, and fruits, to the global market.
We aim to build long-lasting partnerships by guaranteeing the following core elements:
- Superior Quality Assurance: We are confident in our ability to consistently deliver products that meet the highest international quality standards required by the global market.
- The Best Competitive Pricing: We provide high-quality goods at the most competitive prices in the market, helping to optimize the profitability of your import operations.
- Prompt & Dedicated Support: Our team is committed to offering fast, enthusiastic, and professional customer support throughout our entire partnership journey.
If you are interested in importing coconut from Vietnam, please contact us immediately for the best support!
Contact Us Today:
To receive a quotation and detailed assistance, please reach out directly via WhatsApp: +84 979 58 58 56 or LinkedIn: HAVIGO COMPANY LIMITED. We look forward to partnering with you!